(图拉丁)NEOGEO
(图拉丁)NEOGEO

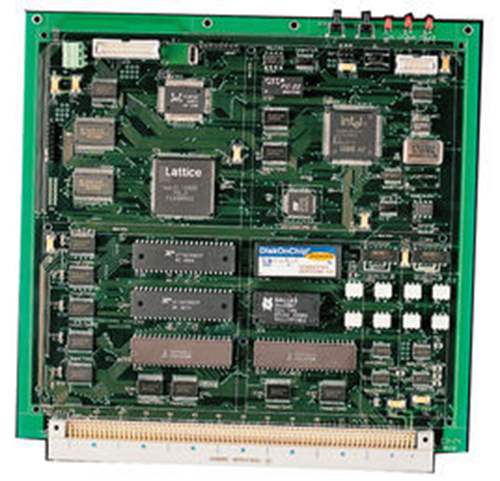
CPU: 摩托罗拉 68000 CPU(16BIT, 10MHz) X 2(两枚) + Z80(处理声音用)
68000处理器,Motorola公司680x0微处理器的鼻祖,是CISC结构,1979年推出,用于最早的Apple Macintosh计算机,以及Apple LaserWriter ⅡSC和Hewlett-Packard公司的LaserJet打印机。68000具有32位内部寄存器,但只能在16位数据总线上传送数据。处理器能访问16兆内存,是IBM PC中Intel 8088的16倍。
68000系列处理器广泛应用于街机中,我们所熟悉的日本街机厂商Capcom、SNK和台湾的IGS,他们生产的街机主板都是采用的68000系列的处理器。
Z80微机的早期应用主要是将构成计算机系统的Z80微处理器,RAM,ROM和输入/出接口等电路都组合在一块PCB板卡上面,因此这时期的Z80微机系统也叫Z80单板机(SBC,Single Board computer)。

1976年美国Zilog公司推出的微处理器(microprocessor)Z840004,Z840006和Z840008因其卓越的性能,强大的输入/出接口能力,快速的运算速度(Z840008时钟频率可达8MHz,同时期的其他产品如Intel的8085、Motorola的M6802等时钟频率为2~5MHz),品种多样的外设支持而迅速被业内人士关注。Zilog公司的这类微处理器通常被叫做Z80微处理器或Z80微机。
Z80单板机具有体积小,外设搭配灵活,运行可靠等特点,因此在以后的十几年时间里,Z80单板机被广泛的应用于PC机接口及扩展和各种工业、控制领域,尤其是在美国和日本得到了极大的发展。我国自上世纪80年代末引入,因为其所具有的第三代计算机的优良特点而迅速被市场所接受,小到家用电器,红白游戏机,大到工业采集系统,自动控制装置,电动机及传动等都有大量的使用和应用。各类大中型院校也开设了Z80微处理器的课程,Z80微处理器和Z80单板机的研究和应用在我国具有广泛的基础。
Zilog公司对Z80微处理器的设计定位是:特殊应用标准产品,即:(Application Specific Standard Parts)。它要求该微处理器既能象ASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)那样尽可能利用硬件设计满足应用对象的各种特殊要求,又能通过软件代码手段来适应各种应用场面。
Z80微处理器使用了NMOS的大规模IC工艺,可以说是当时的Intel 8080的改进产品,为了达成上述设计思想,Z80单板机拥有很多支持的外设,而其支持的汇编指令也多达158条(Intel 8080只有72条),应用非常灵活。
因此,硬件的专门设计+软件的灵活设计构成Z80微处理器的最显著设计特点,也使之成为了80年代最成功的8位CPU之一。
16个地址端口,
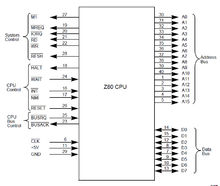
Z80 IO配置
可以寻址64K的地址空间,支持三种中断;具体功能可以参见Z80的datasheet.(z80)
Z80微处理器的内部寄存器也较为特殊,有两套寄存器组:Main Register Set和Alternate Register Set,如图所示。其中Main Register Set完成正常寄存器寻址及运算功能,Alternate Register Set完成对Main Register Set的备份和替换,在实际软件编码中使用很灵活。
Z80的指令集多达158条,按照处理方式可以分成8位指令集和16位指令集;按照功能可以分成8大类;指令的长度一般为1-4字节,执行时间为4-23T,T为时钟周期。
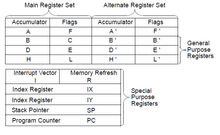
Z80 内部寄存器
Z80寻址方式也很灵活,可以分成:直接寻址,寄存器寻址,寄存器间接寻址,立即寻址,相对寻址和变址寻址,其具体原理可以参见datasheet,这里不再赘述。
虽然Z80微处理器的设计和结构特点已经具备了现代CPU的特点,但由于大规模集成IC工艺的出现,单片机(MCU)这种Soc(System on a Chip)系统的出现对Z80造成了很大的冲击,这表现在:
单片机的大规模集成工艺弥补了Z80单板机的工艺缺陷;
现代工业的高速性使Z80单板机走到了尽头;
单片机的高度外设集成使Z80单板机设计显得复杂;
程序设计的简洁性好和移植性高等特点注定Z80单板机要逐渐被取代;
尽管如此,上世纪80年代左右产生的Z80单板机也是非常优秀的一款微处理器,它在设计之初就已经融入了部分现代CPU的设计理念,并且作为嵌入式学习的一种选择,Z80单板机仍然还是有自己的一些特点:
学习Z80微处理器的硬件结构,寻址方式和指令集有助于理解嵌入式系统开发原理;尽管51,ARM(基于ARM指令集的硬件平台)硬件平台,DSP,AVR,MPS430,9S12,PowerPC等都是非常优秀的嵌入式硬件平台,但究其原理,Z80系统架构仍然是这些架构中的佼佼者,其简洁,灵活的特点是较为显著的;
搭建Z80系统可以更好的理解Soc的工作原理;当前主流的单片机或者Soc系统都采用了大规模集成工艺,对于大多数外设,如RAM,ROM,输入输出端口等都已经集成在了单片机内部,这样就构成了一个类似的“闭锁”系统,再加之C语言开发的特点,很多嵌入式的内部原理是无法深入了解的,而根据嵌入式的特点,只有了解了其内部时序和寄存器的特点(Z80无累加器,使用寄存器阵列的特点)才能开发出优秀的执行率高,误码率少的代码。
内存: 8MB(64Mbits)
Neo-Geo的机能相当强劲,它使用两颗14 Mhz的Motorola 68000CPU,可达320x224的分辨率(最大发色数65,536色,同屏显示4096色),声音处理芯片为Z80A,有8声道的FM合成音源和7声道的数字立体声音源(PSGPCM),系统RAM为7MB(56Mbits).卡带最大容量42MB(330Mbits).
NEO GEO机可能大家比教陌生,但是一定玩过,你们在机室以前玩的饿狼,龙虎之拳,到KOF系列,月华之剑士,越南战役(合金弹头),KOF拳王都是NG机了,不过NG家用机不是很流行,因为NG家用机的主机是和NG街机采用同样的主板和芯片,价格比较贵,NG家用机的游戏软件也同街机一样用NG的ROM带,我见过N

NeoGeo
G街机拆开后里面的确是一盒NG家用机的卡带来的,不过NG家用机还有NG CD的设备,能够玩NG的CD ROM游戏,可以减低成本。
有些朋友认为NG是32位的游戏机,不过其实NG是16位机来的,NG好像没推出过32 BIT的游戏机呢,从NG16一跳跳到NG64了,大家在机室玩的3D的那个立体侍魂就是NG的64 BIT机。
Neo-Geo CD系统发售于1994年9月,是为了解决卡带价格过分昂贵(39800日元,即超过200美元)的问题.所以系统的硬件方面没有大的改变(包括售价),只将卡带读入部分改成了CD-ROM.然而由于Neo-Geo CD 用的是单倍速CD,所以又带来了读盘过于缓慢的问题. 在不久之后的1995年12月,SNK又发售了带二倍速CD-ROM的Neo-Geo CDZ系统,不过CDZ只在日本发卖过.
由于系统的价格不是一般人可以承受的,所以Neo-Geo主机的销量一直不大.但即使是其他厂商也不得不承认Neo-Geo是最强的16位主机.
事过境迁,NEO-GEO所引以为自豪的330Mbits的节目容量因为越来越华丽的游戏而入不敷出了.1998年开始SNK在其卡带上使用了GIGA POWER的压缩技术,使容量达到了400-500Mbits.许多大作得以在NEOGEO上延续下去.
SNK一直致力于制作Neo-Geo所擅长的2D格斗游戏.在全世界范围内这些游戏都相当受欢迎,因此NEOGEO仍是一款成功的主机.
NEOGEO CD主机是由SNK制作的主机,主机平台的知名作品包括KOF系列和合金弹头系列,但是这款主机由于价格过高,而且平台上的开发游戏公司只有SNK一家,所以很快就

NeoGeo
退出了历史的舞台,不过上边的游戏素质还是不错的。
SNK Neogeo CD
CPU: 68000+Z80 16bit CPU
内存: 56M
解象度: 320x224
发色:65,535色
最大发色数:4096色
声音:8-FM synthesis,7-Digital
CD-ROM:2X CD-ROM
SNK NeoGeo CD,1990.4.26发售,拥有几乎所有SNK MVS基板的街机游戏。
NEOGEO CD是著名游戏厂商SNK开发的,其前身是NEOGEO,一款出生于超任时代的主机,俗称机皇,双16位CPU,存储媒体是卡带,大多数游戏都是SNK自己移植的著名街机游戏,比如《格斗之王》、《侍魂》、《饿狼传说》、《合金弹头》等,而NEOGEO CD则是机皇加强版,俗称机皇CD版,采用CD为媒介,无论在画质和音质上都有极大的提高,游戏种类和机皇卡带版差不多,比较出名的有《KOF 97》、《武士道列传》、《月华剑士2》、《天外魔镜真传》等。
NEOGEO的游戏虽然好玩,但是当时由于定价太高,一般玩家实难玩到,再加上基本上它的游戏都是SNK本厂移植的第三方游戏,虽然素质高,可第三方游戏太少,所以它没有大规模普及,有了完美的NEOGEO CD模拟器,大家可以感受这些经典名作的魅力了。
相信有DS的人都在用NeoDS打合金、KOF吧?NeoDS模拟就是SNK于1990年推的大型街机MVS主板,因为开机的时我们都能看到到Neo·Geo,所以大家就把它称之为NeoGeo主机了。其实它有很多版本,像家用机甚至还有掌机,但是都因为市场定位不明确而没能取得成功,不

NeoGeo
过MVS主机板却是被公认为最为成功的一款主机平台,其服役年限之长恐怕也只有拥有怪物软件的GB与之相抗衡一下了(GB系列89~2001),不过如果要说存活时间,恐怕GB也要自叹不如了。街机厅里你仍然能看到它的身影,而且开运行很好,光顾的人也不少。 让我们来看看其究竟有什么本领生存这么长的时间呢?
CPU
两颗16位的Motorola 68000CPU (14Mhz)
内存
7MB
最大发色数
65,536色,同屏显示4096色
最大分辨率
320x224
声音处理芯片
Z80A,拥有8声道的FM合成音源和7声道的数字立体声音源(PSGPCM)
虽然现在看来这些指标可能算不上什么,但是在当时它可是最相当的高配了,特别是当时让它所引以为自豪的330Mbits的节目容量可是最为引人注目的了,也正是因为它的强劲性能,所以在这一主板上才出了许多经典的游戏比如《战国传承》、《KOF》、《合金弹头》……
1994年9月Neo-CD系统发售,虽然是定位于家用机,但是其高昂的定价是大多数人所不能承受的:近650美元。当然其高昂的售价也是因为Neo-CD的硬件基本沿用了其街机主板的配置,只是游戏载体由卡带换成了CD-rom,所以我们也能看到有些地方的街机的机台是由Neo-CD改装而成的。
可以说NeoGeo是SNK的骄傲,特别是在2D格斗方面所取得成绩是当仁不让的关把交椅。只可惜由于后期SNK经营不善走了下坡路,许多的经典游戏也就难以再续其曾经的辉煌了。我们只能用我们手中的DS回味当初热血过的游戏了

Zilog Z80
An early Z80 microprocessor, manufactured in June 1976 according to the date stamp
ProducedFrom March 1976 to presentCommon manufacturer(s)

Mostek, Synertek, Zilog, SGS-Thomson, NEC, Sharp, Toshiba, Rohm, GoldStar, Hitachi, National Semiconductor,[1] and others.

Max. CPU clock rate2.5MHz to 8MHz with CMOS variant up to 20 MHz
A CMOS Z80 in a Quad Flat Package
A May 1976 advertisement for the Zilog Z-80 8-bit microprocessor
The Z80 CPU is an 8-bit based microprocessor. It was introduced by Zilog in 1976 as the startup companys first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his then-11 employees at Zilog from early 1975 until March 1976, when the first fully working samples were delivered. With the revenue from the Z80, the company built its own chip factories and grew to over a thousand employees over the following two years.[2]
The Zilog Z80 was a software-compatible extension and enhancement of the Intel 8080 and, like it, was mainly aimed at embedded systems. According to the designers, the primary targets for the Z80 CPU (and its optional support and peripheral ICs[3]) were products like intelligent terminals, high end printers and advanced cash registers as well as telecom equipment, industrial robots and other kinds of automation equipment. The Z80 was officially introduced on the market in July 1976 and came to be widely used also in general desktop computers using CP/M and other operating systems as well as in the home computers of the 1980s. It was also common in military applications, musical equipment, such as synthesizers, and in the computerized coin operated video games of the late 1970s and early 1980, the arcade machines or video game arcade cabinets.
The Z80 was one of the most commonly used CPUs in the home computer market from the late 1970s to the mid-1980s.[4][5] Zilog licensed the Z80 to the US-based Synertek and Mostek, which had helped them with initial production, as well as to a European second source manufacturer, SGS. The design was copied also by several Japanese, East European and Soviet manufacturers.[6] This won the Z80 acceptance in the world market since large companies like NEC, Toshiba, Sharp, and Hitachi started to manufacture the device (or their own Z80-compatible clones or designs). In recent decades Zilog has refocused on the ever-growing market for embedded systems (for which the original Z80 and the Z180 were designed) and the most recent Z80-compatible microcontroller family, the fully pipelined 24-bit eZ80 with a linear 16MB address range, has been successfully introduced alongside the simpler Z180 and Z80 products.
The Z80 came about when physicist Federico Faggin left Intel at the end of 1974 to found Zilog with Ralph Ungermann. At Fairchild Semiconductor, and later at Intel, Faggin had been working on fundamental transistor and semiconductor manufacturing technology. He also developed the basic design methodology used for memories and microprocessors at Intel and led the work on the Intel 4004, the 8080 and several other ICs. Masatoshi Shima, the principal logic and transistor level-designer of the 4004 and the 8080 under Faggins supervision, also joined the Zilog team.
By March 1976, Zilog had developed the Z80 as well as an accompanying assembler based development system for its customers, and by July 1976, this was formally launched onto the market.[7] (Some of the Z80 support and peripheral ICs were under development at this point, and many of them were launched during the following year.)
Early Z80s were manufactured by Synertek and Mostek, before Zilog had its own manufacturing factory ready, in late 1976. These companies were chosen because they could do the ion implantation needed to create the depletion-mode MOSFETs that the Z80 design used as load transistors in order to cope with a single 5 Volt power supply.[8]
Faggin designed the instruction set to be binary compatible with the Intel 8080[9][10] so that most 8080 code, notably the CP/M operating system and Intels PL/M compiler for 8080 (as well as its generated code), would run unmodified on the new Z80 CPU. Masatoshi Shima designed most of the microarchitecture as well as the gate and transistor levels of the Z80 CPU, assisted by a small number of engineers and layout people.[11][12] CEO Federico Faggin was actually heavily involved in the chip layout work, together with two dedicated layout people. Faggin worked 80 hours a week in order to meet the tight schedule given by the financial investors, according to himself.[13]
The Z80 offered many improvements over the 8080:[10]
An enhanced instruction set[14] including single-bit addressing, shifts/rotates on memory and registers other than the accumulator, rotate instructions for BCD number strings in memory, program looping, program counter relative jumps, block copy, block input/output (I/O), and byte search instructions.[15] The Z80 also incorporated an overflow flag and had better support for signed 8- and 16-bit arithmetics.[16]
New IX and IY index registers with instructions for direct base+offset addressing
A better interrupt system
A more automatic and general vectorized interrupt system, mode 2, primarily intended for Zilogs line of counter/timers, DMA and communications controllers, as well as a fixed vector interrupt system, mode 1, for simple systems with minimal hardware (with mode 0 being the 8080-compatible mode).[17]
A non maskable interrupt (NMI) which can be used to respond to power down situations or other high priority events (and allowing a minimalistic Z80 system to easily implement a two-level interrupt scheme in mode 1).
Two separate register files, which could be quickly switched, to speed up response to interrupts such as fast asynchronous event handlers or a multitasking dispatcher. Although they were not intended as extra registers for general code, they were nevertheless used that way in some applications.[18]
Less hardware required for power supply, clock generation and interface to memory and I/O
Single 5-volt power supply (the 8080 needed -5V/+5V/+12V).
Single-phase 5V clock (the 8080 needed a high-amplitude (9 to 12 volt) non-overlapping two-phase clock).
A built-in DRAM refresh mechanism that would otherwise have to be provided by external circuitry.[19]
Non-multiplexed buses (the 8080 had state-signals multiplexed onto the data bus).
A special reset function which clears only the program counter so that a single Z80 CPU could be used in a development system such as an in-circuit emulator.[20]
The Z80 took over from the 8080 and its offspring, the 8085, in the processor market,[21] and became one of the most popular 8-bit CPUs.[4][5] Perhaps a key to the initial success of the Z80 was the built-in DRAM refresh, and other features which allowed systems to be built with fewer support chips (Z80 embedded systems typically use static RAM and hence do not need this refresh).
For the original NMOS design, the specified upper clock frequency limit increased successively from the introductory 2.5MHz, via the well known 4MHz (Z80A), up to 6 (Z80B) and 8MHz (Z80H).[22][23] CMOS versions were also developed with specified upper frequency limits ranging from 4MHz up to 20MHz for the version sold today. The CMOS versions also allowed low-power sleep with internal state retained, having no lower frequency limit.[24] The fully compatible derivatives HD64180/Z180[25][26] and eZ80 are currently specified for up to 33 and 50MHz respectively.
ps0178-19386.pdf






以上就是((图拉丁)NEOGEO)全部内容,收藏起来下次访问不迷路!